Prog8 - Structured Programming Language for 8-bit 6502/6510 microprocessors
Written by Irmen de Jong (irmen@razorvine.net)
Software license: GNU GPL 3.0, see file LICENSE
This is a structured programming language for the 8-bit 6502/6510 microprocessor from the late 1970's and 1980's as used in many home computers from that era. It is a medium to low level programming language, which aims to provide many conveniences over raw assembly code (even when using a macro assembler):
- reduction of source code length
- easier program understanding (because it's higher level, and more terse)
- option to automatically run the compiled program in the Vice emulator
- modularity, symbol scoping, subroutines
- subroutines have enforced input- and output parameter definitions
- various data types other than just bytes (16-bit words, floats, strings, 16-bit register pairs)
- automatic variable allocations, automatic string variables and string sharing
- constant folding in expressions (compile-time evaluation)
- automatic type conversions
- floating point operations
- abstracting away low level aspects such as ZeroPage handling, program startup, explicit memory addresses
- breakpoints, that let the Vice emulator drop into the monitor if execution hits them
- source code labels automatically loaded in Vice emulator so it can show them in disassembly
- conditional gotos
- various code optimizations (code structure, logical and numerical expressions, ...)
It is mainly targeted at the Commodore-64 machine at this time.
Documentation is online at https://prog8.readthedocs.io/
Required tools:
64tass - cross assembler. Install this on your shell path. A recent .exe version of this tool for Windows can be obtained from my clone of this project. For other platforms it is very easy to compile it yourself (make ; make install).
A Java runtime (jre or jdk), version 8 or newer is required to run the packaged compiler. If you want to build it from source, you'll need a Kotlin 1.3 SDK as well (or for instance, IntelliJ IDEA with the Kotlin plugin).
It's handy to have a C-64 emulator or a real C-64 to run the programs on. The compiler assumes the presence of the Vice emulator
Example code
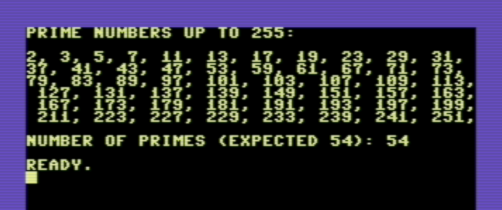
This code calculates prime numbers using the Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm::
%import c64utils
%zeropage basicsafe
~ main {
ubyte[256] sieve
ubyte candidate_prime = 2
sub start() {
memset(sieve, 256, false)
c64scr.print("prime numbers up to 255:\n\n")
ubyte amount=0
while true {
ubyte prime = find_next_prime()
if prime==0
break
c64scr.print_ub(prime)
c64scr.print(", ")
amount++
}
c64.CHROUT('\n')
c64scr.print("number of primes (expected 54): ")
c64scr.print_ub(amount)
c64.CHROUT('\n')
}
sub find_next_prime() -> ubyte {
while sieve[candidate_prime] {
candidate_prime++
if candidate_prime==0
return 0
}
sieve[candidate_prime] = true
uword multiple = candidate_prime
while multiple < len(sieve) {
sieve[lsb(multiple)] = true
multiple += candidate_prime
}
return candidate_prime
}
}
when compiled an ran on a C-64 you'll get:
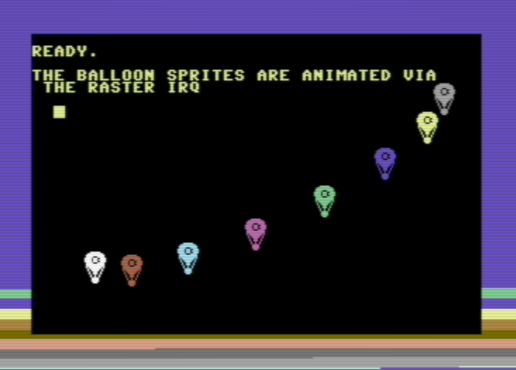
One of the included examples (wizzine.p8) animates a bunch of sprite balloons and looks like this:
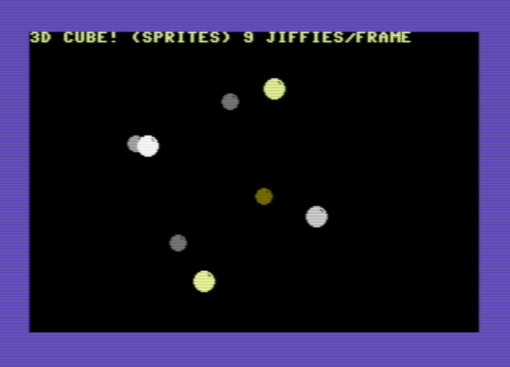
Another example (cube3d-sprites.p8) draws the vertices of a rotating 3d cube:
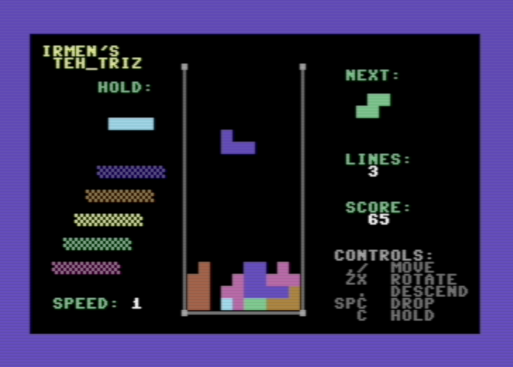
If you want to play a video game, a fully working Tetris clone is included in the examples: